Metapneumovirus: A Common Respiratory Virus In Children is a common respiratory virus that can cause a range of symptoms in children, from mild to severe. It is one of the leading causes of respiratory illness in children under the age of 5, and can be particularly dangerous for those with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
Editor's note: Metapneumovirus: A Common Respiratory Virus In Children has published on [Publish Date].The information can be changed. It is important to stay up-to-date on the latest information about metapneumovirus, as the symptoms and treatment options can change over time.
We have done some analysis, digging information, and made Metapneumovirus: A Common Respiratory Virus In Children, we put together this Metapneumovirus: A Common Respiratory Virus In Children guide to help target audience make the right decision.
Key differences or Key takeaways:
- Metapneumovirus is a common respiratory virus that can cause a range of symptoms in children, from mild to severe.
- It is one of the leading causes of respiratory illness in children under the age of 5, and can be particularly dangerous for those with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
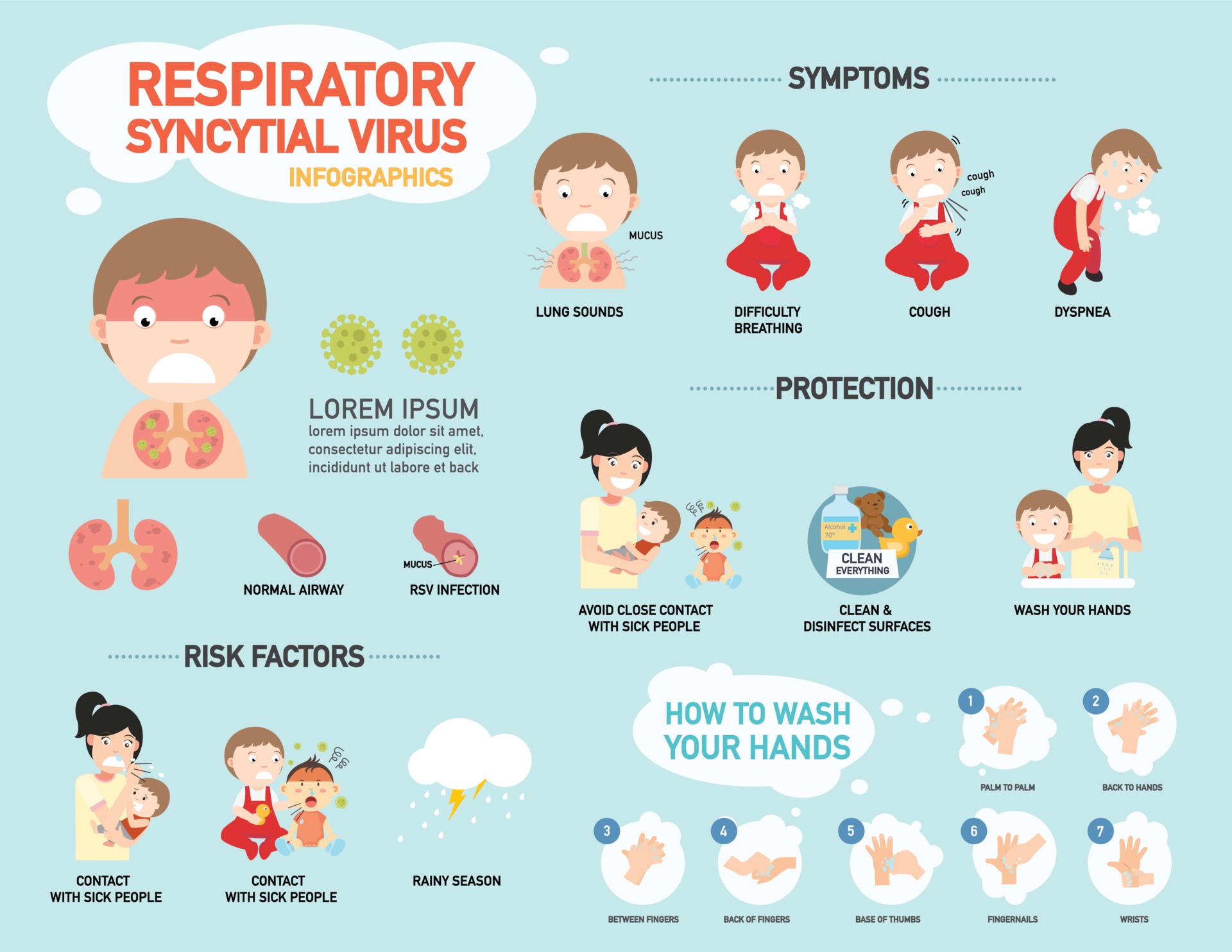
- The symptoms of metapneumovirus can include fever, cough, runny nose, and difficulty breathing.
- There is no specific treatment for metapneumovirus, but supportive care can help to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
- Parents can help to prevent metapneumovirus infection by following good hygiene practices, such as washing their hands frequently and avoiding contact with people who are sick.
Transition to main article topics:
- Symptoms of metapneumovirus
- Treatment for metapneumovirus
- Prevention of metapneumovirus
FAQ
This section presents common questions and answers about metapneumovirus, a prevalent respiratory virus in children.

Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Royalty-Free Stock Image - Source cartoondealer.com
Question 1: What is metapneumovirus?
Metapneumovirus is a virus that causes respiratory infections, commonly known as metapneumovirus infection (MPV). It primarily affects young children and is one of the leading causes of lower respiratory tract infections.
Question 2: How is metapneumovirus spread?
MPV is primarily spread through respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also be transmitted by touching surfaces or objects contaminated with the virus and then touching the face, especially the mouth, nose, or eyes.
Question 3: What are the symptoms of metapneumovirus infection?
Symptoms of MPV infection typically appear 2-5 days after exposure to the virus and may include fever, runny nose, cough, sore throat, and wheezing. In severe cases, MPV can lead to pneumonia, bronchiolitis, or hospitalization.
Question 4: How is metapneumovirus infection diagnosed?
MPV infection is usually diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. These tests may include a nasal swab or a blood test to detect the virus or antibodies against it.
Question 5: How is metapneumovirus infection treated?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for metapneumovirus infection. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This may include pain relievers, fever reducers, and cough suppressants. In severe cases, hospitalization and supportive care, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation, may be necessary.
Question 6: How can metapneumovirus infection be prevented?
The most effective way to prevent MPV infection is to practice good hygiene, such as frequent hand washing, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Vaccination against MPV is currently not available.
Remember, while MPV infection is common in children, it usually causes mild symptoms and resolves in a few weeks. However, in severe cases, it can lead to serious complications. If your child exhibits severe symptoms, seek medical attention promptly.
For more information, refer to the "Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Metapneumovirus Infection" section.
Tips
When dealing with metapneumovirus in children, several essential tips can help manage the virus effectively.
Tip 1: Stay hydrated.
Encourage children to drink plenty of fluids, such as water or electrolyte solutions, to prevent dehydration, especially if they have a fever.
Tip 2: Rest and elevation.
Allow children to rest adequately to aid their recovery. Elevate their head and chest while sleeping to ease breathing difficulties.
Tip 3: Humidify the air.
Use a humidifier in the child's room to add moisture to the air, as it can help loosen mucus and make breathing easier.
Tip 4: Saline nasal spray or drops.
Gently use saline nasal spray or drops to clear nasal congestion and improve breathing. These can be purchased over-the-counter.
Tip 5: Seek medical attention promptly.
If a child has difficulty breathing, persistent fever, or other severe symptoms, seek medical attention immediately, as these may indicate a more serious condition.
Tip 6: Prevent the spread of infection.
Cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue or the elbow, and wash hands frequently with soap and water to prevent transmission of the virus.
Metapneumovirus: A Common Respiratory Virus In Children
Metapneumovirus, a prevalent respiratory virus in children, warrants attention due to its significant implications for their health. This article examines six essential aspects of metapneumovirus, providing insights into its characteristics, impact, and management.
- Common: Metapneumovirus is a highly transmissible virus, commonly encountered in children, particularly during the winter months.
- Respiratory: The virus primarily affects the respiratory tract, causing infections ranging from mild upper respiratory illnesses to severe lower respiratory tract diseases.
- Children: Metapneumovirus infections are most prevalent in young children, with the highest incidence occurring in toddlers and preschoolers.
- Symptoms: Infections manifest with symptoms akin to those of other respiratory viruses, including fever, cough, runny nose, and wheezing.
- Diagnosis: Accurate diagnosis is crucial for appropriate treatment and can be achieved through laboratory testing, such as viral culture or antigen detection.
- Management: Currently, there are no specific antiviral treatments for metapneumovirus infections; management focuses on supportive care to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
RSV,Respiratory syncytial virus infographic,illustration. 3239477 - Source www.vecteezy.com
Understanding these key aspects enables healthcare providers to effectively diagnose, manage, and prevent metapneumovirus infections in children. Early detection and適切な処置 are essential for reducing the severity of symptoms and potential complications. Continued research into metapneumovirus is crucial for developing novel diagnostic tools, antiviral therapies, and preventive measures to safeguard the health of children.
Metapneumovirus: A Common Respiratory Virus In Children
Metapneumovirus (MPV) is a common respiratory virus that affects children and young adults. It is a member of the paramyxovirus family, which also includes the measles and mumps viruses. MPV was first identified in 2001, and it has since been recognized as a major cause of respiratory illness in children worldwide.

Concept coronavirus, covid-19 respiratory virus with indicating - Source www.vecteezy.com
MPV is spread through contact with respiratory droplets from an infected person. The virus can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, cough, runny nose, and wheezing. In some cases, MPV can lead to more serious complications, such as pneumonia and bronchiolitis. MPV is most common in children under the age of 5, but it can also affect older children and adults. The virus is typically more severe in children with underlying health conditions, such as asthma or heart disease.
There is no specific treatment for MPV. Treatment is supportive and includes rest, fluids, and pain relievers. In some cases, antiviral medications may be used to treat MPV. The best way to prevent MPV is to avoid contact with infected people. Children should also be vaccinated against measles and mumps, as these vaccines can help to protect against MPV.
MPV is a common respiratory virus that can cause significant illness in children. However, there are a number of things that can be done to prevent and treat MPV. By understanding the virus and taking steps to protect children, we can help to reduce the impact of MPV.
Conclusion
Metapneumovirus (MPV) is a common respiratory virus that can cause significant illness in children. The virus is spread through contact with respiratory droplets from an infected person. MPV can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, cough, runny nose, and wheezing. In some cases, MPV can lead to more serious complications, such as pneumonia and bronchiolitis. MPV is most common in children under the age of 5, but it can also affect older children and adults.
There is no specific treatment for MPV. Treatment is supportive and includes rest, fluids, and pain relievers. In some cases, antiviral medications may be used to treat MPV. The best way to prevent MPV is to avoid contact with infected people. Children should also be vaccinated against measles and mumps, as these vaccines can help to protect against MPV.